Commutative Property
- Commutative Property
- Commutative Property of Addition
- Commutative Property of Multiplication
- Solved Examples on Commutative Property
- Practice Problems On Commutative Property
- Frequently Asked Questions On Commutative Property
Introduction:
The commutative property is a fundamental property in mathematics that applies to both addition and multiplication. This property states that changing the order of the terms or factors in an expression does not change the result.
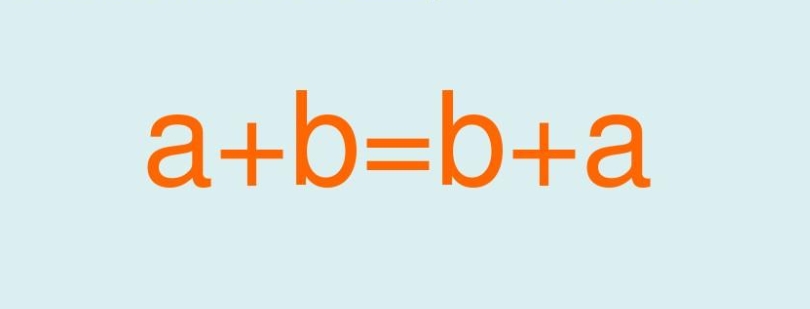
Commutative Property of Addition:
The commutative property of addition states that the sum of two or more numbers is the same regardless of the order in which they are added. For example, if we have the numbers 5, 7, and 9, the commutative property allows us to add them in any order:
5 + 7 + 9 = 21 9 + 7 + 5 = 21 7 + 5 + 9 = 21
In all three cases, the result is 21. This property holds true for any numbers and is a key concept in basic arithmetic.
Commutative Property of Multiplication:
The commutative property of multiplication states that the product of two or more numbers is the same regardless of the order in which they are multiplied. For example, if we have the numbers 2, 3, and 4, the commutative property allows us to multiply them in any order:
2 X 3 X 4 = 24
4 X 3 X 2 = 24
3 X 2 X 4 = 24
 In all three cases, the result is 24. This property holds true for any numbers and is a fundamental concept in multiplication.
In all three cases, the result is 24. This property holds true for any numbers and is a fundamental concept in multiplication.
Solved Examples on Commutative Property:
- Example for Commutative Property of Addition: Let's consider the numbers 8, 4, and 3.
8 + 4 + 3 = 15 4 + 8 + 3 = 15
No matter the order in which the numbers are added, the result will always be 15.
- Example for Commutative Property of Multiplication: Let's consider the numbers 2, 5, and 6.
2 X 5 X 6 = 60 5 X 2 X 6 = 60
The order in which the numbers are multiplied does not affect the result, which is 60 in both cases.
Practice Problems On Commutative Property:
- Practice Problem for Commutative Property of Addition: Solve the following addition problems to demonstrate the commutative property:
a) 3 + 7 + 9 b) 9 + 3 + 7 c) 7 + 9 + 3
- Practice Problem for Commutative Property of Multiplication: Solve the following multiplication problems to demonstrate the commutative property:
a) 4 X 8 X 2 b) 2 X 4 X 8 c) 8 X 2 X 4
Frequently Asked Questions On Commutative Property:
1. What is the commutative property?
The commutative property states that changing the order of terms or factors in an expression does not change the result. This property applies to both addition and multiplication.
2. How does the commutative property work in addition?
The commutative property of addition states that the sum of two or more numbers is the same regardless of the order in which they are added.
3. How does the commutative property work in multiplication?
The commutative property of multiplication states that the product of two or more numbers is the same regardless of the order in which they are multiplied.
4. Are there any other mathematical operations where the commutative property applies?
The commutative property also applies to other operations such as binary operations in abstract algebra, but is most commonly associated with addition and multiplication.
5. Does the commutative property apply to subtraction or division?
No, the commutative property does not apply to subtraction or division. For example, 5 - 3 is not the same as 3 - 5, and 10 ÷ 2 is not the same as 2 ÷ 10.
Conclusion
The commutative property is a fundamental concept in mathematics that applies to both addition and multiplication. It states that changing the order of terms or factors in an expression does not change the result. This property is widely used in various mathematical operations and is a key concept in basic arithmetic. Understanding and applying the commutative property is essential for solving mathematical problems accurately and efficiently.